Drias, Yassine
Loading...
Profile URL
Name Variants
Job Title
Email Address
driasy@mef.edu.tr
Main Affiliation
02.02. Department of Computer Engineering
Status
Current Staff
Website
ORCID ID
Scopus Author ID
Turkish CoHE Profile ID
Google Scholar ID
WoS Researcher ID
Sustainable Development Goals
2
ZERO HUNGER

3
Research Products
16
PEACE, JUSTICE AND STRONG INSTITUTIONS

0
Research Products
1
NO POVERTY

0
Research Products
11
SUSTAINABLE CITIES AND COMMUNITIES

1
Research Products
7
AFFORDABLE AND CLEAN ENERGY

0
Research Products
10
REDUCED INEQUALITIES

0
Research Products
3
GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

0
Research Products
6
CLEAN WATER AND SANITATION

0
Research Products
9
INDUSTRY, INNOVATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE

1
Research Products
12
RESPONSIBLE CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION

2
Research Products
5
GENDER EQUALITY

0
Research Products
14
LIFE BELOW WATER

0
Research Products
13
CLIMATE ACTION

1
Research Products
15
LIFE ON LAND

0
Research Products
8
DECENT WORK AND ECONOMIC GROWTH

2
Research Products
17
PARTNERSHIPS FOR THE GOALS

0
Research Products
4
QUALITY EDUCATION

0
Research Products

Documents
44
Citations
107
h-index
6

Documents
27
Citations
60

Scholarly Output
14
Articles
2
Views / Downloads
1839/1
Supervised MSc Theses
1
Supervised PhD Theses
0
WoS Citation Count
3
Scopus Citation Count
3
WoS h-index
1
Scopus h-index
1
Patents
0
Projects
0
WoS Citations per Publication
0.21
Scopus Citations per Publication
0.21
Open Access Source
0
Supervised Theses
1
| Journal | Count |
|---|---|
| -- 33rd IEEE Conference on Signal Processing and Communications Applications, SIU 2025 -- Istanbul; Isik University Sile Campus -- 211450 | 3 |
| 32nd IEEE Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU) -- MAY 15-18, 2024 -- Tarsus Univ Campus, Mersin, TURKEY | 2 |
| Symposium on Quantum Sciences, Applications and Challenges (QSAC) -- SEP 24-25, 2023 -- Alger Acad Sci & Tech, Algiers, ALGERIA | 2 |
| Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems -- 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, ISDA 2023 -- 11 December 2023 through 13 December 2023 -- Olten -- 315609 | 1 |
| Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems -- 7th International Conference on Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, INFUS 2025 -- Istanbul – 336089 | 1 |
Current Page: 1 / 2
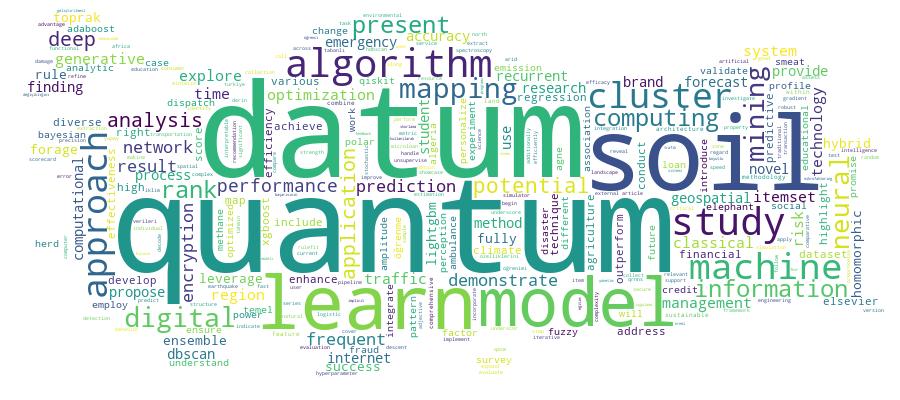
Competency Cloud